interstitial fluid measuring less than 1 mm thick|interstitial fluid in human body : factories What is interstitial fluid? Our body distributes about 40 liters (about 10 gallons) of fluid in three main fluid “compartments:” intracellular fluid (28 liters), blood (4.6 liters), and interstitial fluid .
web20 de set. de 2023 · Official announcements for The-Elite forums, rankings, and events. Posts: 133 Topics: 10. Last post: September 20, 2023, 11:22:33 AM Re: Proof Policy, .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB29 de out. de 2020 · Esse termo em inglês pode ser traduzido como “esquadrão”, em referência às unidades de militares que são enviados a um combate. Assim como um .
In UC College of Engineering and Applied Science professor Jason Heikenfeld’s Novel Devices Lab, students are developing sensors to measure hormones and other chemicals in interstitial fluid. They use . Interstitial fluid (ISF) surrounds cells within tissue. It is the medium through which cells receive nutrients, secrete waste and communicate through molecular signals. By volume, . Evidence for interstitial pulmonary edema is also provided by an increase in the thickness of the walls of bronchi seen end-on in the perihilar zones. In the absence of chronic . • Microneedle sensors enable minimally invasive and continuous biomarker monitoring through dermal interstitial fluid. • This review offers a comprehensive overview of .
Small calcified nodules refer to nodular opacities measuring less than 10 mm in diameter that have focal of diffuse calcification evident on high-resolution CT. .What is interstitial fluid? Our body distributes about 40 liters (about 10 gallons) of fluid in three main fluid “compartments:” intracellular fluid (28 liters), blood (4.6 liters), and interstitial fluid . Peripheral biochemical monitoring involves the use of wearable devices for minimally invasive or noninvasive measurement of analytes in biofluids such as interstitial fluid, .The effective oncotic pressure difference determining fluid balance in filtering microvessels is greater when calculated using the oncotic pressure in the subglycocalyx region (π c − π g) .
Basic differences between the two forms of measurement. Interstitial fluid glucose changes are measured by CGM devices in a small volume of tissue around the tip of the glucose sensor, which undergoes . The total thickness of the pork skin was roughly 12.7 mm. Edema is usually first observed in lower limbs, and the average subcutaneous tissue thicknesses in the legs are 10.79 mm in males and 12.44 mm in females, . The Revised Principle highlights the role of oncotic pressure of small volumes of interstitial fluid within a sub-compartment surrounding the microvessels rather than the tissue's mean .
terstitial fluid pressure at +1 mm Hg. When the mean interstitial fluid pressure in the two catheters approached zero, and especially when this mean value rose into the positive range, only 0.5 mm Hg pressure differential was applied between the two catheters be-cause the rate of fluid flow between the two catheters became much too great for .The interstitial fluid is found in the interstitial spaces, also known as the tissue spaces. On average, a person has about 11 liters (2.4 imperial gallons or about 2.9 U.S. gal) of interstitial fluid that provide the cells of the body with nutrients and a means of waste removal. The physiological range in human skin is (less than) 1 to 4 mm 10,15 and 1 to 12 mm 23 for the dermis and adipose tissue, respectively. The thickness of the epidermis on a human forearm is 36–61 μm. 24 On the wrist, this thickness can increase to almost 100 μm. 24 Therefore, we tested a thickness of 50 and 100 μm.
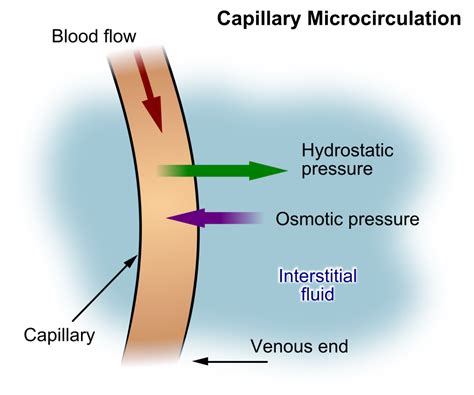
Blood vessel density in the invasive front (peripheral MVD) was determined by counting vessels located within a 1-mm-thick band in the tumor periphery (Figure 1, A and B). Peritumoral density of lymphatics [peritumoral lymph vessel density (LVD)] was assessed by counting vessels in the surrounding skin located within a distance of 0.5 mm from .The forces that tend to move fluid out from the capillaries are the P CAP (about 20 mm Hg), the COP IF (about 8 mm Hg) and the P IF, which is normally negative (−1 to −3 mm Hg). So there is . The pleura is a double-layered membrane composed primarily of mesothelial cells that surround each lung (visceral pleura) and line the thoracic cavity (parietal pleura) (Fig. 1).The potential space between the 2 layers (pleural space) normally contains a physiologic amount of pleural fluid (approximately 5 cc) which allows the parietal and visceral pleura to slide over . Thus, it is highly desirable to find a new way to measure glucose in body fluids as a supplement to blood glucose measurement. In recent years, skin interstitial fluid (ISF) has been considered an alternative source of biomarkers , due to the reliable correlation between blood glucose levels and the level found in ISF [7,8].
testing interstitial fluid
Ozerdem and Hargens Page 6 NIH-PA Author Manuscript Fig. 1. Interstitial fluid pressure measurement with ultraminiature pressure transducer. (A) The ultraminiature transducer (arrow) is introduced percutaneously 1 mm through the tumor capsule into the superficial tumor in a protective metal guide (18-gauge needle) (arrowhead).Methods to measure, model and manipulate fluid flow in brain. Krishnashis Chatterjee, . Jennifer M. Munson, in Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2020 2.2.3 Interstitial fluid flow. The interstitial space within the cerebral tissue also has fluid flow within it, though this flow is much slower than that of CSF or CBF, leading to many molecules moving more by diffusion then .The initial high-resolution CT findings consist of numerous high-attenuation nodules measuring less than 1 mm in diameter or diffuse ground-glass . and systemic disorders. The interstitial dystrophic pulmonary ossification can be localized or distributed widely. Dendriform pulmonary ossification, defined as widespread heterotopic . Subcutaneous interstitial fluid pressure (P i) was measured in anesthetized rats with the “wick-in-needle” technique: A thin hypodermic needle was provided with a 2- to 4-mm-long sidehole and filled with multifilamentous nylon thread.A polyethylene tube, connecting the needle to a pressure transducer, could be compressed by a screw clamp, displacing a volume .
Cavities can heal and end up as lungcysts and lungcysts can become infected and turn into thick walled cavities. Sometimes emphysematous bullae have visible walls that measure less than 1 mm. To differentiate them .
Extracellular fluid (ECF) surrounds all cells in the body. Extracellular fluid has two primary constituents: the fluid component of the blood (called plasma) and the interstitial fluid (IF) that surrounds all cells not in the blood (Figure .
The flow of interstitial fluid in tissues like bone, tendon, meniscus and possibly other tissue types is similar to blood flow in the vascular system in the sense that the different pore size porosities are nested, but unsimilar in three important aspects; (1) there are only two levels of pore size porosity important for bone fluid flow, (2 . The Guyton chamber allows for an accurate measurement of interstitial fluid pressure without the interference from various cellular/tissue components. . For 1-mm**2 10- mu m-thick diaphragms in .
Introduction. Postmenopausal vaginal bleeding is a common complaint and is associated with a 1–10% risk of endometrial cancer, depending on age and risk factors 1, 2.Because the risk of cancer is relatively high, the clinical standard of care requires diagnostic evaluation to exclude malignancy 2, 3.Until the 1980s, fractional dilation and curettage was the . smaller loosely organized bundles of collagen at 45° angle to the long axis of the tendon (3 mm thick) Layer IV. loose connective tissue and thick collagen bands and merges with fibers from coracohumeral ligament. Layer V. shoulder capsule (2 mm thick) . less than 1% incidence. Usually common skin flora: staph aureus, strep, p.acnes.
During this phase, the endometrium begins to thicken and may measure between 10–16 mm. About 14 days into a person’s cycle, hormones trigger the release of an egg.
At the present time, there are no methods for measuring the solid parts of the interstitium; they are probably composed of materials more like those of the interstitial fluid than those of the intracellular fluid, but the exact composition is not known. 5. Composition and Mass of the Interstitial Fluid: This fluid is like plasma in its composition.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has the potential to greatly improve diabetes management. The aim of this work is to show a proof-of-concept CGM device which performs minimally invasive and minimally delayed in-situ glucose sensing in the dermal interstitial fluid, combining the advantages of microneedle-based and commercially available CGM systems. .At an interstitial fluid pressure of greater than zero (i.e., values greater than the alveolar pressure), the tissue fluid accumulates with only a small change in the interstitial pressure. The high-compliance portion of the curve may represent the transition from interstitial edema to alveolar edema 62 ; that is, the pressure inflection point . The increasing demand for minimal to noninvasive in situ analysis of body fluids, such as sweat, interstitial fluid, and tears, has driven rapid development of electrochemically active materials .
The real part ε ′ was influenced by the mobility and the quantity of the electric dipoles. The imaginary part ε ″ described conductive and dipole losses.. Modelling goal was to find the most optimal arrangement of the electrodes enabling to measure the biggest difference in impedance and capacitance, which depend on increase of the interstitial fluid. To study the effect of flow on interstitial cells, we place a mast cell (a sphere with a diameter of 16 μm) in the center of the domain (the center of the sphere is at x = 2 mm, y = z = 0 mm) (Figure 1(b)).The magnified mast cell in Figure 1(b) shows the local Cartesian coordinates O′x′y′z′. The origin (O′) is at the center of the sphere, and the x′-axis, y′-axis and z′-axis .
fatigue testing machine name

interstitial fluid vs blood work
web4 de nov. de 2016 · Bowling alley and lounge with auto-scoring, leagues, birthday parties and karaoke nights. 790 Yonkers Avenue, 914 969-2417. Cortlandt Lanes Inc. The lane offers cosmic bowling, fall and summer .
interstitial fluid measuring less than 1 mm thick|interstitial fluid in human body